56.
Which statement defines session hijacking most accurately?
- A.Session hijacking involves stealing a user’s login information and using that information to pose as the user later.
- B.Session hijacking involves assuming the role of a user through the compromise of physical tokens such as common access cards.
- C.Session hijacking is an attack that aims at stealing a legitimate session and posing as that user while communicating with the web resource or host machine.
- D.Session hijacking involves only web applications and is specific to stealing session IDs from compromised cookies.
- Answer & Explanation
- Report
Answer : [C]
Explanation :
Explanation :
| Session hijacking focuses on the victim’s session. There are different ways of accomplishing this task, but the basic concept is the same. Be sure to know what constitutes a session hijack; the exam will expect you to be able to recognize one at first glance. |
57.
Jennifer has been working with sniffing and session-hijacking tools on her company
network. Since she wants to stay white hat—that is, ethical—she has gotten permission
to undertake these activities. What would Jennifer’s activities be categorized as?
- A.Passive
- B.Monitoring
- C.Active
- D.Sniffing
- Answer & Explanation
- Report
Answer : [A]
Explanation :
Explanation :
| Julie is operating in the passive sense in this scenario. Sniffing traffic is a passive activity. |
58.
Based on the diagram, what attack is occurring?
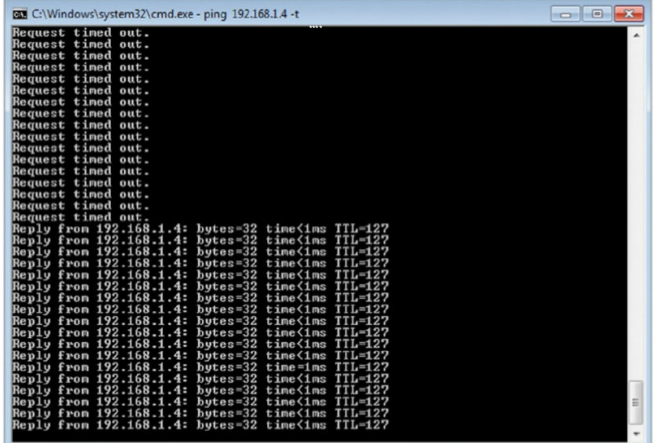
- A.Session splicing
- B.Denial-of-service
- C.Source routing
- D.MITM
- Answer & Explanation
- Report
Answer : [D]
Explanation :
Explanation :
| Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks are an exam favorite; just remember that the broader category of session hijacking encompasses MITM attacks. Anytime you see a computer placed in the middle, you should immediately suspect MITM or session hijacking. |
59.
Jennifer is a junior system administrator for a small firm of 50 employees. For the last
week a few users have been complaining of losing connectivity intermittently with no
suspect behavior on their part such as large downloads or intensive processes.
Jennifer runs Wireshark on Monday morning to investigate. She sees a large amount
of ARP broadcasts being sent at a fairly constant rate. What is Jennifer most likely
seeing?
- A.ARP poisoning
- B.ARP caching
- C.ARP spoofing
- D.DNS spoofing
- Answer & Explanation
- Report
Answer : [A]
Explanation :
Explanation :
| An excessive number of ARP broadcasts would indicate an ARP poisoning attack. The users’ reporting loss of connectivity may indicate an attempted session hijacking with a possible DoS attack. |
60.
Which of the following is not a source of session IDs?
- A.URL
- B.Cookie
- C.Anonymous login
- D.Hidden login
- Answer & Explanation
- Report
Answer : [C]
Explanation :
Explanation :
| URLs, cookies, and hidden logins are all sources of session IDs. |
- Pages
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40