-
General Knowledge
-
General Topics
- Abbreviations
- Books and Authors
- Famous Academies and Institutes
- First in India (Man)
- First in India (Women)
- Important Dates
- Famous Personalities
- Public Administration Science
- Astronomy
- Biology
- Botany
- Chemistry
- Physics
- Zoology
- Inventions and Scientists Geography
- Geographical Epithets India
- Geographical Epithets World
- Places Associated with Industries in India
- National Parks and Sanctuaries
- Towns on River Banks History
- Indian History and Culture
- Indian National Movement
- Indian Polity and Constitution
- Ancient Period in Indian History
- World History
- Governor General of India Culture
- Languages
- Indian Dance and Music
- Classical Dances of India
- Folk Dances in India and Tribal Dances in India
- Famous Dancers, Instrumentalists, Vocalists in India World
- First in the World
- Parliament Names
- United Nation Organizations (UNO)
- World's Famous News Agencies
- World Industries
- National Emblems
- Countries and Alternative Names
- Countries and Capitals
- View More topics...
- General Aptitude
- Problems on Ages
- Alligation and Mixture
- Area
- Arithmetic Progression
- Average
- Banker's Discount
- Boats and Streams
- Calendar
- Chain Rule
- Clock
- Compound Interest
- Decimal Fraction
- Height and Distance
- Logarithms
- Mensurations
- Numbers
- Odd Man Out and Series
- Partnership and Share
- Percentage
- Permutation and Combination
- Pipes and Cisterns
- Probability
- Problems on H.C.F and L.C.M
- Problems on Numbers
- Problems on Trains
- Profit and Loss
- Races and Games
- Ratio and Proportion
- Simple Interest
- Simplification
- Stocks and Shares
- Surds and Indices
- Time and Distance
- Time and Work
- True Discount
- Volume & Surface Areas
- General English
- Antonyms
- Synonyms
- Vocabulary Test
- One Word Substitution
- Sentence Completion
- Sentence Improvement
- Idioms & Phrases
- Homonyms
- Word Formation
- Active & Passive Voice
- Direct and Indirect Speech
- Spotting Errors
- Double Synonyms
- Choose the Appropriate Filter
- Spelling Test
- Transformation
- Reconstruction of Sentence
- Chooose the Correct or Incorrect Sentence
- Networking
- Interview Questions
-
Programming
- .NET
- Java
- ASP.NET
- C++
- Perl
- Python
- Ruby and Rails
- Struts
- Core Java
- Hibernate Database
- DB2
- MS SQL Server
- MySQL
- Oracle
- SQL
- DBMS
- Data Warehousing
- Data structures and Algorithms Cisco
- CCNA
- CCNP Routing
- CCNP Switching
- Internetworking
- Border Gateway Protocol Windows
- MCSE
- Exchange Server
- Windows Server 2008
- DNS & Active Directory
- Firewall Questions Linux
- Unix
- Linux Server Administrator
- Linux System Administrator
- Linux File Manipulation
- Database
- Home
- Online-Quiz
- Networking
- CCNP Route
Instructions
- Total Questions 20
- Each question carry 1 mark
- Must answer all the questions (otherwise report card will not be generated)
- If you dont want to take a test, simply click the check answers button and view all the answers with explanations
- Do Not Refresh the Page
- No Time Limit
- Good Luck :)
You Scored % - /
Correct Answers :
[D]
Explanation :
Inside a quartet, any leading 0s can be omitted, and one sequence of one or more quartets of all 0s can be replaced with “::”. The correct answer replaces the longer three-quartet sequence of 0s with ::.
Correct Answers :
[C]
Explanation :
The name of the prefix generally represents the group to which the prefix is given, with the exception of the term global routing . IANA assigns a prefix to a registry (registry prefix). The registry can assign a subset of that range as a prefix to an ISP (ISP prefix). That ISP then subdivides that range of addresses into prefixes and assigns a prefix to one of its customers (site prefix, also called global routing prefix). The enterprise network engineers then further subdivide the range, often with prefix length 64, into subnet prefixes.
Correct Answers :
[B]
Explanation :
An outside global address represents a device outside of a network with a globally
routable address. In this scenario, the web server’s IP address of 203.0.113.10 would be
an outside global address.
An inside local address represents a device inside of a network with an address that
is not routable on the public Internet. In this scenario, the laptop’s IP address of
10.1.1.241 would be an inside local address.
An inside global address represents a device on the inside of our network with an
address that is a globally routable address. In this scenario, the laptop’s translated
address of 198.51.100.54 would be an inside global address.
An outside local address represents a device on the outside of a network that has an
address that is not routable on the public Internet. For example, if NAT were being performed
at a remote site, the destination device at the remote site would have an outside
local address. In the scenario presented in this question, there is no outside local address.
Correct Answers :
[A]
Explanation :
An outside global address represents a device outside of a network with a globally
routable address. In this scenario, the web server’s IP address of 203.0.113.10 would be
an outside global address.
An inside local address represents a device inside of a network with an address that
is not routable on the public Internet. In this scenario, the laptop’s IP address of
10.1.1.241 would be an inside local address.
An inside global address represents a device on the inside of our network with an
address that is a globally routable address. In this scenario, the laptop’s translated
address of 198.51.100.54 would be an inside global address.
An outside local address represents a device on the outside of a network that has an
address that is not routable on the public Internet. For example, if NAT were being performed
at a remote site, the destination device at the remote site would have an outside
local address. In the scenario presented in this question, there is no outside local address.
Correct Answers :
[B]
Explanation :
ICANN and IANA manage the assignment of public IPv4 address space such that large address blocks (often called CIDR blocks) exist in a particular geography or are assigned to particular ISPs. As such, Internet routers can more easily create summary routes to help keep the routing table small in the Internet. 200.1.2.0/24 would likely also be allocated to some registrar, ISP, or customer in Asia. Because of the large route summaries, in this case possibly a summary for 200.0.0.0/8, routers in North America would not see an increase in the size of their routing tables.
Correct Answers :
[D]
Explanation :
The question asks which answers are true about the eBGP peer but also not true about an iBGP peer. Both iBGP and eBGP use TCP port 179. An eBGP peer uses a different ASN than the local router, by definition, making that answer incorrect. The correct answer refers to the fact that an eBGP peer adds its own ASN to the BGP AS_Path PA before sending routing information to another router, whereas iBGP peers do not.
Correct Answers :
[D]
Explanation :
Three of the commands list valid commands. The neighbor 2.2.2.2 multihop 2 command is syntactically incorrect; it should be neighbor 2.2.2.2 ebgp-multihop 2 .
Correct Answers :
[D]
Explanation :
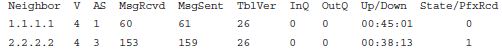
The show ip bgp command lists the BGP neighbor state in the last column of output, listing the literal state, unless in an established state. In that state, the output lists the number of prefixes learned from the neighbor, so a numeric value implies an established state.
Correct Answers :
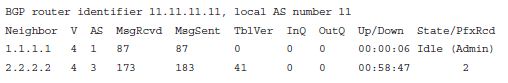
[A and D]
Explanation :
The output lists R2's local ASN as ASN 11, a value that is configured in the router bgp asn command. The line for neighbor 1.1.1.1 lists that router's ASN as 1, so a neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 1 command should exist on R2 instead of the neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 11 command. The state for neighbor 1.1.1.1 lists "Idle (Admin)," implying that the neighbor 1.1.1.1 shutdown command has been configured. The other answer lists a nonexistent command.
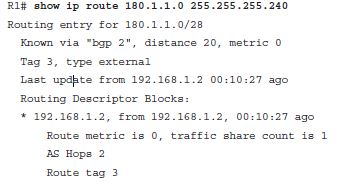
Correct Answers :
[C]
Explanation :
The "Known via" text refers to the local router's (R1's) router bgp command, which identifies the local router’s ASN. The rest of the output does not identify the neighboring ASN, nor the rest of the AS_Path details. It does list that the route is external, with the text "type external" and the AS Hops (which is the AS_Path length).

Correct Answers :
[D]
Explanation :
The small letter "i" in the third character position implies that the route was learned with iBGP. Of the five lines, four have an "i" in the third column.

Correct Answers :
[B and C]
Explanation :
The line reading “1.1.1.1 from 2.2.2.2...” implies the BGP RID of the neighbor is 1.1.1.1, with neighbor ID—the IP address on the local router’s neighbor command—of 2.2.2.2. The end of the output shows that the route is internal (iBGP learned) and is best, so both the > and i will be displayed for this route by the show ip bgp command. Finally, the output does not identify the local ASN, although it does list the AS_Path of the route (1, 2, 3, 4).
Correct Answers :
[B]
Explanation :
The show ip bgp neighbors 2.2.2.2 advertised-routes command does list the post-outbound-filter BGP Update; however, the user did not issue a clear command, so the filter has not yet taken effect. As such, the output still lists the original three prefixes as if the filter had not yet been applied.
Correct Answers :
[B and D]
Explanation :
Weight, a Cisco-proprietary feature of BGP on Cisco routers, cannot be transmitted in a BGP Update, so setting Weight on an outbound route map at the ISPs will have no effect. Also, the goals call for setting Weight for all routes from an ISP to the same number, so creating a prefix list to match a subset of reachable prefixes, in this case all Class C networks, is not useful. However, two methods of configuring Weight do exist: the neighbor weight command and configuring an inbound route map with a set weight command in the route map.

Correct Answers :
[B]
Explanation :
The output shows the results of AS_Path prepending. The repetitive 1s cannot mean that the route has been advertised into and out of the same ASN repeatedly because loop prevention would have prevented such an advertisement. With AS_Path prepending, the neighboring ASN typically adds its own ASN to the end of the AS_Path (as listed on the left of the output).

Correct Answers :
[C]
Explanation :
The command lists the administrative distance as the first number inside the square brackets and the MED values as the second number in brackets. The AD of 20 implies an eBGP route instead of iBGP. The output says nothing about the Weight or AS_Path length.
Correct Answers :
[D]
Explanation :
The ipv6 route ::/0 next_hop_ipv6_address command is used to create a default static IPv6 route.

Correct Answers :
[B]
Explanation :
When configuring IPv6 routing over an IPv4 BGP session, you need to create a route map that specifies the local router interface’s IPv6 address as the next-hop IPv6 address to advertise to its neighbor. However, this step is not a requirement when configuring IPv6 routing over an IPv6 BGP session.
Correct Answers :
[A and B]
Explanation :
The only valid options after ipv6 prefix-list LIST1 seq 10 permit 2000::/16 are le (meaning less than or equal to) and ge (meaning greater than or equal to). The number of bits in the prefix length then follows those options.

Correct Answers :
[C]
Explanation :
The AS path length and weights are the same for both next hops. However, the next-hop IPv6 address of 2000:3::2 has a higher Local Preference (150) than 2000:2::2 (50). Therefore, 2000:3::2 is chosen as the best next hop (as indicated with the ">" sign).
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||